Mechanism of muscle contraction pdf
View and Download PowerPoint Presentations on Mechanism Of Musle Contraction PPT. Find PowerPoint Presentations and Slides using the power of XPowerPoint.com, find free presentations research about Mechanism Of Musle Contraction PPT
Jun 09, 2017 · Muscle contraction animation #Please→Like, comment, share and subscribe ️
Jun 20, 1969 · The Mechanism of Muscular Contraction. By H. E. Huxley. See all Hide authors and affiliations. Science 20 Jun 1969: Vol. 164, Issue 3886, pp. 1356-1366 Info & Metrics; eLetters; PDF; This is a PDF-only article. The first page of the PDF of this article appears above. Science. Vol 164, Issue 3886 20 June 1969 . Table of Contents ; Back
Muscular contraction is essentially the shortening of the S 2 subunits of heavy meromyosin, integrated to macroscopic motion by the thick and thin filaments. Full text Get a printable copy (PDF file) of the complete article (365K), or click on a page image below to browse page by page.
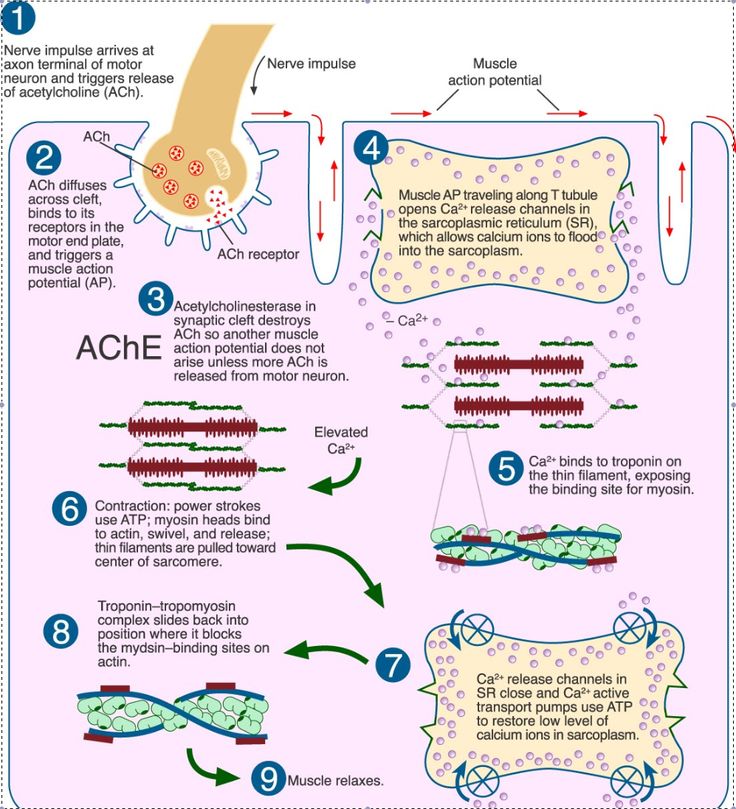
Mechanism of muscle contraction: During relaxation, myosin cross-bridges separate from actin and actin filaments slide back from A-bands. Calcium is an essential element for the contraction of muscles. During muscle contraction, chemical energy is changed into mechanical energy.
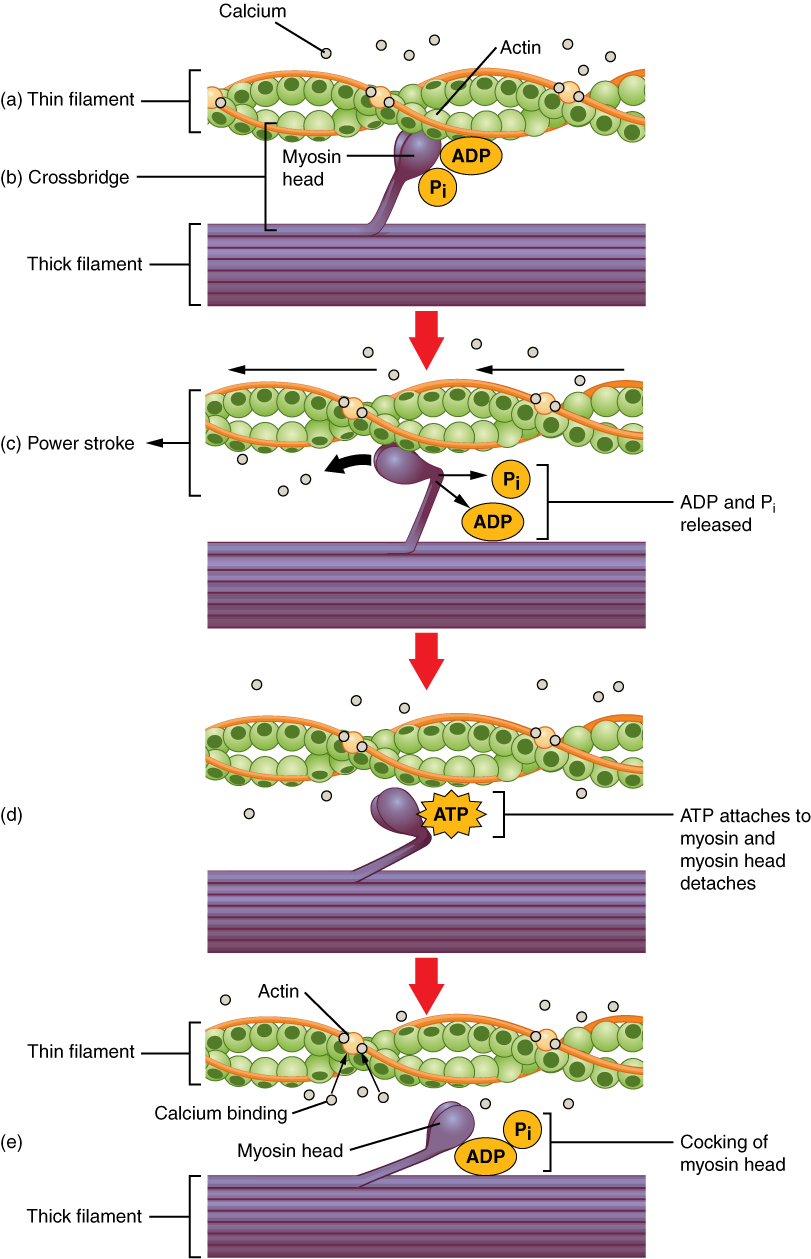
ATP and Muscle Contraction. For thin filaments to continue to slide past thick filaments during muscle contraction, myosin heads must pull the actin at the binding sites, detach, re-cock, attach to more binding sites, pull, detach, re-cock, etc. This repeated movement is known as the cross-bridge cycle.
focused on elucidating the specific mechanisms involved in excitation-contraction (EC) coupling – the mechanism that controls Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) and the consequent muscle contraction – in hopes of gaining an understanding of the role of the EC process in health and disease.
Muscle contraction 2 • Multiple fiber summation – When a weak signal is sent by the CNS to contract a muscle, the smaller motor units, being more excitable than the larger ones, are stimulated first. As the strength of the signal increases, more motor units are excited in addition to larger ones, with the largest motor units having as much as 50 times the
X-ray crystallography shows the myosin cross-bridge to exist in two conformations, the beginning and end of the “power stroke.” A long lever-arm undergoes a 60° to 70° rotation between the two states. This rotation is coupled with changes in the active site (OPEN to CLOSED) and phosphate release. Actin binding mediates the transition from CLOSED to OPEN. Kinetics shows that the binding
Start studying Mechanisms of Skeletal Muscle Contraction. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
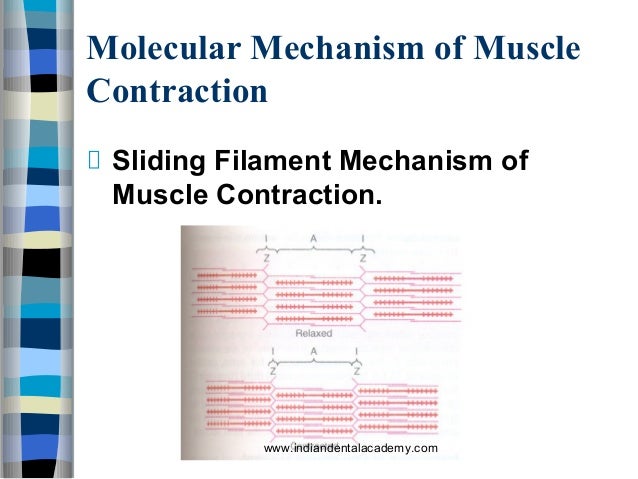
Sep 09, 2018 · Mechanism of muscle contraction Sliding – filament hypothesis Hanson and Huxley proposed this hypothesis (1955). According to this hypothesis, the contractile unit of muscle is made up of two types of filaments
What is the Sliding Filament Theory of muscular contraction?. The sliding filament theory is the explanation for how muscles contract to produce force. As we have mentioned on previous pages, the actin and myosin filaments within the sarcomeres of muscle fibres bind to create cross-bridges and slide past one another, creating a contraction.
Mar 21, 2008 · Thus, treating physicians should be aware of the mechanisms of muscle pain, insofar as they are currently understood. This article provides an overview of the more common types of muscle pain. It is not intended as a comprehensive guide to all that is known about muscle pain, including both basic research and clinical aspects.
General mechanism of muscle contraction SlideShare
MUSCLE University of Minnesota
The object of this paper is to trace the growth of a fundamental problem that for a decade hindered the development of several lines of muscle research: the molecular mechanism that allows and
of contraction in striated muscle have gained general *acceptance and it has been possible to concentrate attention on the detailed mechanism by which the relative sliding force between the actin and myosin filaments is devel-oped. Anumber of observations have indicated in general outline how cross-bridges between the filaments may be involved
The Sliding Filament Mechanism of Muscle Contraction(4) second molecule of ATP attaches to ATP-binding site on myosin head, which allows it to detach from actin filament; a new cross bridge forms along thin filament and generates another power stroke
Mechanism of smooth muscle contraction Article · Literature Review (PDF Available) in Physiological Reviews 76(4):967-1003 · November 1996 with 9,504 Reads How we measure ‘reads’
Muscle contraction is the activation of tension-generating sites within muscle fibers. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length such as holding a heavy book or a …
Summary. Muscle contraction occurs when the thin actin and thick myosin filaments slide past each other. It is generally assumed that this process is driven by cross-bridges which extend from the myosin filaments and cyclically interact with the actin filaments as ATP is hydrolysed.
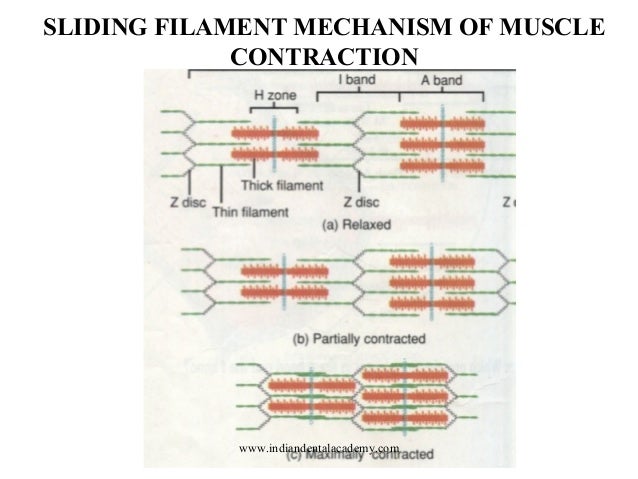
tal muscle fiber, the overlapping thick and thin filaments in each sarcomere move past each other, propelled by movements of the cross-bridges. During this shortening of the sarcomeres, there is no change in the lengths of either the thick or thin filaments (Figure 9–8). This is known as the sliding-filament mechanism of muscle contraction.
This book describes the evolution of ideas relating to the mechanism of muscular contraction since the discovery of sliding filaments in 1954. An amazing variety of experimental techniques have been employed to investigate the mechanism of muscular contraction and relaxation. Some background of
Cardiac muscle fibers contract via excitation-contraction coupling, using a mechanism unique to cardiac muscle called calcium -induced calcium release. Excitation-contraction coupling describes the process of converting an electrical stimulus ( action potential ) into a mechanical response (muscle contraction).
A mechanism of muscle contraction is presented in which energy from the hydrolysis of MgATP is transferred directly to conformational strain in a flex…
Cardiac excitation-contraction coupling (Cardiac EC coupling) describes the series of events, from the production of an electrical impulse (action potential) to the contraction of muscles in the heart. This process is of vital importance as it allows for the heart to beat in a controlled manner, without the need for conscious input.

Jan 22, 2012 · Sliding Filament Mechanism of Muscle Contraction• Muscle contraction occurs by a sliding filament mechanism.• When action potential travels along the muscle fiber, sarcoplasmic reticulum release large quantities of calcium ions that rapidly surround the myofibrils.• Energy is needed for the contractile process to proceed.
Muscle Contraction Fall, 2010 PEP 426: Muscle Contraction & ATP Demand 4 Skeletal Muscle Contraction Excitability – receive and propagate an action potential. Contractility – contract/shorten Elasticity – rapidly return to a pre-contraction length. The demands of exercise require that skeletal muscles must be
that occur preceding the actual contraction of a skeletal muscle. b) Period of contraction –actin causing the shortening of macromere and the contraction of muscle. c) period of relaxation-actin returns to its original position, causing the lengthening of sarcomeres and the relaxation of muscle.
Muscle Contraction and Movement Chapter 30 Muscles Muscles are attached to bones by tendons Muscles work in antagonistic pairs Ex. Biceps and triceps One muscle contracts while the other relaxes Contractile apparatus Skeletal muscle Muscle cell = muscle fiber (a single cell with one nucleus) Muscle fibers are made of myofibrils (striated) Myofibrils are made of units called sarcomeres
In this special issue we present several invited original and review articles from researchers who study muscle structure and function from different perspectives and emphases. During the last decades we have seen a major revision of the immutable postulates …
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd. Flag for inappropriate content. save Save Mechanism of Muscle Contraction For Later. Info. Embed. Share. Print. Related titles. Carousel Previous Carousel Next. Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and Dreams.
This regulatory mechanism appears to be of unique importance in smooth muscle compared with striated muscle. It is equally clear, however, that there is an important role for protein kinase C in the regulation of smooth muscle tone maintenance, particularly in vascular smooth muscle.
Abstract——The smooth muscle cell directly drives the contraction of the vascular wall and hence regu-lates the size of the blood vessel lumen. We review here the current understanding of the molecular mecha-nisms by which agonists, therapeutics, and diseases regulate contractility of …
Nov 29, 2015 · Mechanism and Types of muscle contraction. Mechanism of muscle contraction.. I. Sliding – filament hypothesis. Hanson and Huxley proposed this hypothesis (1955). According to this hypothesis, the contractile unit of muscle is made up of two types of filaments i.e., myosin and actin.
Notes: Muscle Contraction The Basic Unit of Muscle Contraction is the Sarcomere. Skeletal and cardiac muscle are striated (smooth muscle has a similar contractile mechanism but is not so highly organized and does not show striations)
Mechanism of Muscular Contraction Jack A. Rall Springer
Mar 14, 2017 · Sliding Filament Theory of Muscle Contraction. The mechanism of muscle contraction is explained by sliding filament model. This theory was proposed by H.E Huxley and J. Hanson, and A. F. Huxley and R. Niedergerke in 1954.
Mar 01, 2014 · Mechanism Of Muscle Contraction Step 7. The electrical impulse stimulates the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release calcium into the (a contractile unit of a mofibril) area. 12. Mechanism Of Muscle Contraction Step 8. Calcium bind with tropnin-C and activates myosin ATPase. As myosin ATPase become active.
Annual Review of Biophysics and Bioengineering The Molecular Basis of Muscle Contraction M Young Annual Review of Biochemistry Active Transport of Calcium Ion in Sarcoplasmic Membranes Giuseppe Inesi Annual Review of Biophysics and Bioengineering Special Topic: Molecular Mechanism of Muscle Contraction Y. E. Goldman and B. Brenner
The swinging–cross-bridge theory for muscle contraction envisages that the myosin cross-bridge binds to the actin filament in an initial conformation and then undergoes a swinging motion that “rows” the actin filament along (10). Myosin is a product-inhibited ATPase with an active site and mechanism similar to that of the G-proteins (18).
Publisher Summary This chapter describes the analysis of the polymorphism of the myosin crossbridge and relates it to the Lymn–Taylor crossbridge cycle. Myosin from muscle (myosin II) consists of two long polypeptide chains (heavy chains) combined with four light chains. In cross-striated muscle, the tails of the molecules pack together to form the thick filaments, while the crossbridges
Apr 30, 2018 · At the foundation of all movement is the humble muscle cell. If you remember from biology, there are quite a few steps to a simple muscle contraction, so we’ll do our best to simplify it in this article. There are plenty of resources to explain the sliding filament theory and the makeup of a muscle cells and sarcomeres. Like here and hereNov 23, 2010 · Mechanism of Skeletal muscle contraction When a head attaches to an active site, this attachment simultaneously causes profound changes in the intramolecular forces between the head and arms of its cross-bridge.
The whole process is called the mechanism of muscle contraction and it can be summarized in three steps: (1) A message travels from the nervous system to the muscular system, triggering chemical reactions. (2) The chemical reactions lead to the muscle fibers reorganizing themselves in a way that shortens the muscle–that’s the contraction.
Mechanism of Muscle Contraction – Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Mekanisme kontraksi otot
Jun 06, 2017 · Muscle Contraction Process (BEST EXPLANATION EVER) – Molecular Mechanism 3D Animation 1 The Mechanism of Muscle Contraction: Sarcomeres, Contraction of Skeletal Muscle – Duration: 13:37
Sliding Filament Mechanism in Muscle Contraction: Fifty Years of Research covers the history of the sliding filament mechanism in muscle contraction from its discovery in 1954 by H.E. Huxley through and including modern day research.Chapters include topics in dynamic X-ray diffraction, electron microscopy, muscle mechanisms, in-vitro motility assay, cardiac versus smooth muscle, motile systems
The contraction of skeletal muscles by electrical stimulation can produce a muscle contraction capable of aiding lymphatic and venous flow. The intervention can be enhanced further by combining it with other forms of management, such as elevation, cryotherapy, rest, and compression. Muscle pumping protocols are valuable for pain modulation.
Mechanism of muscle contraction Padeepz
Mechanism Of Musle Contraction PPT Xpowerpoint
Physiology of Muscle Contractions Flashcards Quizlet
The Physiology of Skeletal Muscle Contraction — PT Direct
The Mechanism of Muscular Contraction
EDITORIAL Mechanisms of Excitation Contraction Coupling in

Mechanism of Muscle Contraction Muscle Contraction
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gastrointestinal_physiology
Notes Muscle Contraction Easy Peasy All-in-One High School
Muscle Contraction Process [HD Animation] YouTube
Muscle Contraction an overview ScienceDirect Topics

The mechanism of muscle contraction Sliding filament
Molecular Mechanism of Contraction Annual Review of
Notes: Muscle Contraction The Basic Unit of Muscle Contraction is the Sarcomere. Skeletal and cardiac muscle are striated (smooth muscle has a similar contractile mechanism but is not so highly organized and does not show striations)
General mechanism of muscle contraction SlideShare
The whole process is called the mechanism of muscle contraction and it can be summarized in three steps: (1) A message travels from the nervous system to the muscular system, triggering chemical reactions. (2) The chemical reactions lead to the muscle fibers reorganizing themselves in a way that shortens the muscle–that’s the contraction.
Mechanism of Muscle Contraction Muscle Contraction
The mechanism of muscle contraction Sliding filament
Muscle Contraction and Movement Chapter 30 Muscles Muscles are attached to bones by tendons Muscles work in antagonistic pairs Ex. Biceps and triceps One muscle contracts while the other relaxes Contractile apparatus Skeletal muscle Muscle cell = muscle fiber (a single cell with one nucleus) Muscle fibers are made of myofibrils (striated) Myofibrils are made of units called sarcomeres
(PDF) The Molecular Mechanism of Muscle Contraction
Sliding Filament Mechanism in Muscle Contraction
Molecular Mechanism of Muscle Contraction New
Sliding Filament Mechanism in Muscle Contraction: Fifty Years of Research covers the history of the sliding filament mechanism in muscle contraction from its discovery in 1954 by H.E. Huxley through and including modern day research.Chapters include topics in dynamic X-ray diffraction, electron microscopy, muscle mechanisms, in-vitro motility assay, cardiac versus smooth muscle, motile systems
Muscle contraction Wikipedia
The mechanism of muscle contraction. Biochemical
Nov 23, 2010 · Mechanism of Skeletal muscle contraction When a head attaches to an active site, this attachment simultaneously causes profound changes in the intramolecular forces between the head and arms of its cross-bridge.
Physiology of Muscle Contractions Flashcards Quizlet
The Sliding Filament Mechanism of Muscle Contraction(4) second molecule of ATP attaches to ATP-binding site on myosin head, which allows it to detach from actin filament; a new cross bridge forms along thin filament and generates another power stroke
Mechanism of Skeletal Muscle Contraction Medchrome
Mechanism of Muscle Contraction Scribd
Notes: Muscle Contraction The Basic Unit of Muscle Contraction is the Sarcomere. Skeletal and cardiac muscle are striated (smooth muscle has a similar contractile mechanism but is not so highly organized and does not show striations)
Muscle contraction Wikipedia
This regulatory mechanism appears to be of unique importance in smooth muscle compared with striated muscle. It is equally clear, however, that there is an important role for protein kinase C in the regulation of smooth muscle tone maintenance, particularly in vascular smooth muscle.
Muscle Contraction Process (BEST EXPLANATION EVER
The Mechanism of Muscle Contraction